

Compared to other energy sources, hydropower as a regenerative energy can meet the requirements of environmental and climate protection, economic efficiency, service life and reliability in a special way. This is supported by the frequent multiple use of hydropower plants for purposes such as navigation, flood protection and local recreation. In addition, hydropower is the only technology that can be used to date to store energy on a large scale for short-term retrieval. By providing such balancing power, hydropower also has an important support function for the use of other renewable energies. In addition, hydropower plants play a role in the security of grid operation and reconstruction after disruptions.
In the planning of hydropower plants, the interaction between the disciplines of civil engineering, hydraulic engineering, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and river ecology plays a decisive role. Numerous questions have to be answered by hydraulic engineering. For example, the hydraulically optimized design of the inflow situation, the design of the suction hose and the underwater area as well as the achievement of passability for fish.
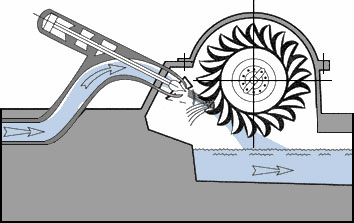
The department offers scientific accompanying investigations by means of various modeling and simulation techniques, whereby data can also be collected by means of natural measurement campaigns for the assessment of operationally relevant issues.







