Chair of Hydraulic Engineering

Chair - Task Areas
At the Chair, we are engaged in basic research as well as research and development contracts to develop engineering solutions in the following areas:

Methods Used

Experimental Hydraulic Engineering
Experimental hydraulic engineering is dedicated to the investigation of hydraulic and hydromechanical fundamentals, processes and relationships. The findings and results of such investigations are used for the development of new formulae and new design and calculation methods as well as for the derivation of required empirical coefficients, e.g. for the extension of the application range of proven formulae. The data can also be used to calibrate and validate numerical calculation methods. The essential requirement for such investigations is the knowledge of the boundary conditions and the exact conditionability of the test conditions.
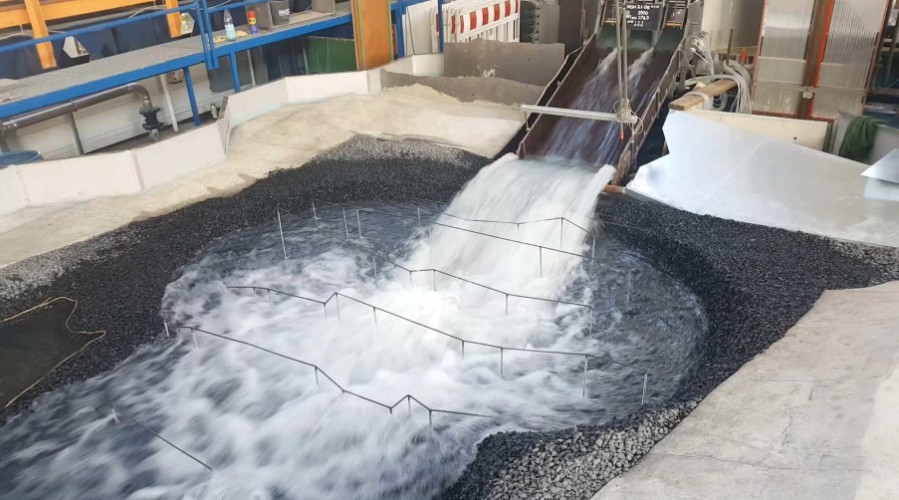

Physical Models
Physical models represent plans or the existing situation of real hydraulic engineering facilities and/or systems at a reduced scale. By means of similarity-mechanical relationships, parameters and processes recorded in the model can be transferred to the natural situation. In this way, the hydraulic functionality of hydraulic engineering systems can be optimally investigated and system optimizations can be tested on the basis of the discernible interactions. For physical models, a structure surface, a water supply and discharge system as well as measurement, control and regulation technology are required.
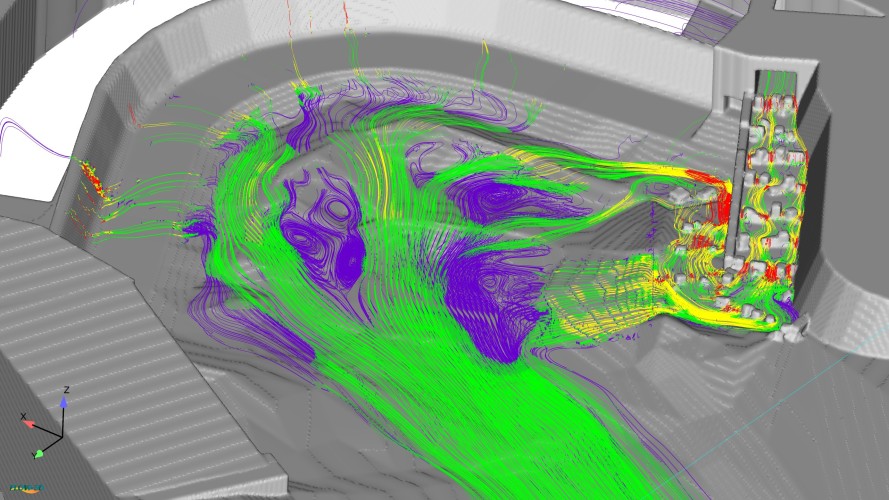
Numerical Models
Mathematical equation systems and their numerical solution form the core of numerical modeling. Often, these are the conservation laws of mass, momentum and, if necessary, energy, which are balanced at the edges of infinitesimal model units in order to derive information on flow behavior, water levels and other hydromechanical parameters for the modeled area. Numerical models always work with simplifications, which result from the spatial, temporal and mathematical discretization and, if necessary, are supplemented by simplifying turbulence models. Therefore, concrete statements are only possible after careful calibration and validation.
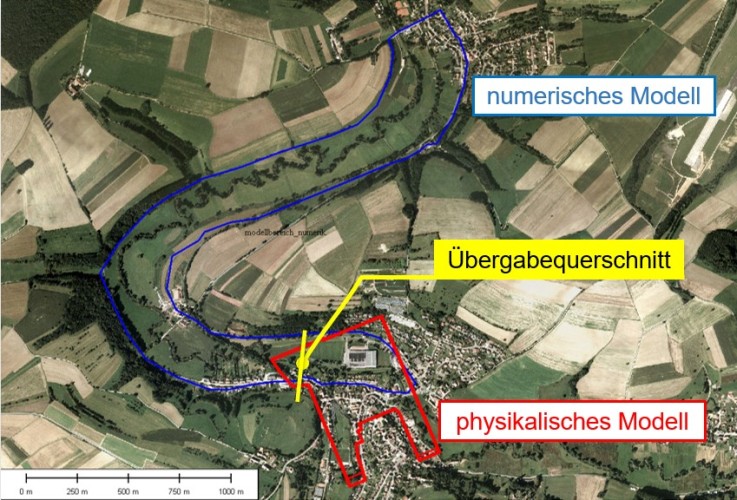
Hybrid Models
Hybrid models combine the strengths of physical and numerical models by coupling both types of models. The type of coupling plays an important role. For example, the holistic investigation of the function and impact of a hydraulic engineering facility in a watercourse can be accomplished for the near field of the facility with high accuracy by a physical model, and the impact in the far field of the facility can be accomplished with a large-scale numerical model. The coupling of both models can be done by value exchange in a defined transfer cross section.
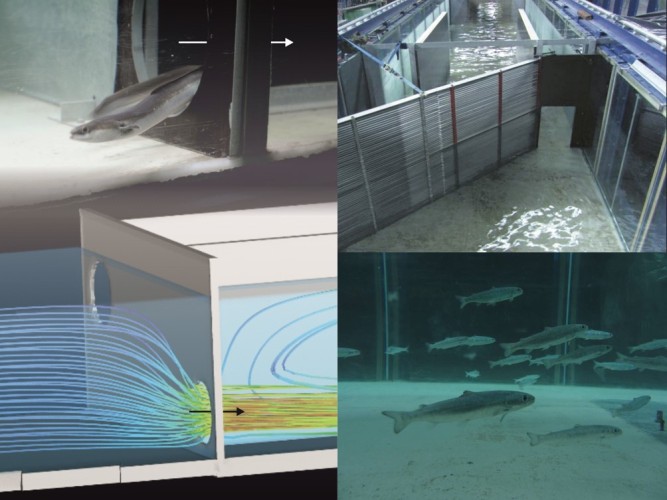
Ethohydraulic Models
The interface between comparative behavioral research and hydraulics forms the basis for ethohydraulic studies. Large laboratory flumes with (modular) internals and known hydraulic situations are used here. Aquatic animals are used here and their hydraulic-reactive behavior is investigated. From the findings and results obtained, limit and guideline values can be derived for the animal-compatible planning of hydraulic engineering facilities (e.g. fishways) as well as concrete design specifications (e.g. for fish protection and fishways).
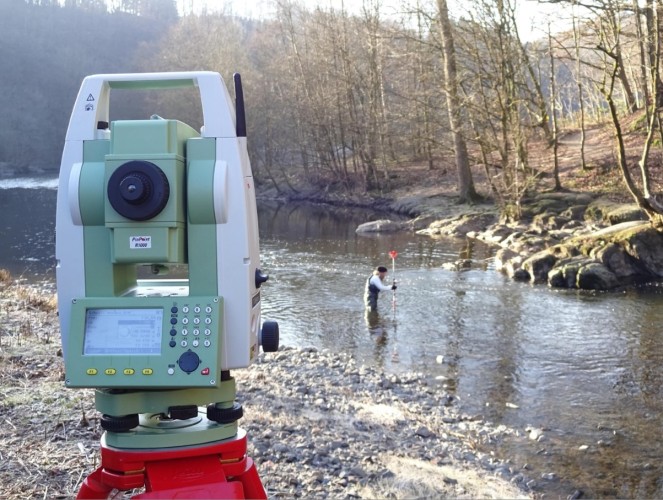

Field Measurement Campaigns
Field measurement campaigns provide important input and calibration data for physical and numerical models. In addition, the data collected during field measurement campaigns help to evaluate the functionality of existing facilities or to identify deficiencies and their causes. Both hydrometric and geodetic measurement procedures and methods are used here.









